Troubleshooting
This section has some tips on troubleshooting if you are having problems.
CeruleanTracker is equipped with many tooltips to help you use the app and to help determine status. Make use the window is active (click on the title bar) and then hover the cursor over any of the controls.
Generally, the best troubleshooting sequence is to make sure the receiver/transceiver is working, then make sure the transmitter is working, then see if the system is working.
If you are going through a troubleshooting guide and can't continue due to errors, please see this.
Here is an example of an unstructured quick troubleshooting session. A quick first thing to to is look at the ROVL Rx tab on the CeruleanTracker main window (example below). The example shows the user is trying to select COM port 6 to talk to the ROVL receiver (or transceiver). Looking at the bottom of the window, it appears that CeruleanTracker is not detecting COM port 6. Looking at the status details, there are some issues listed that might cause the error.
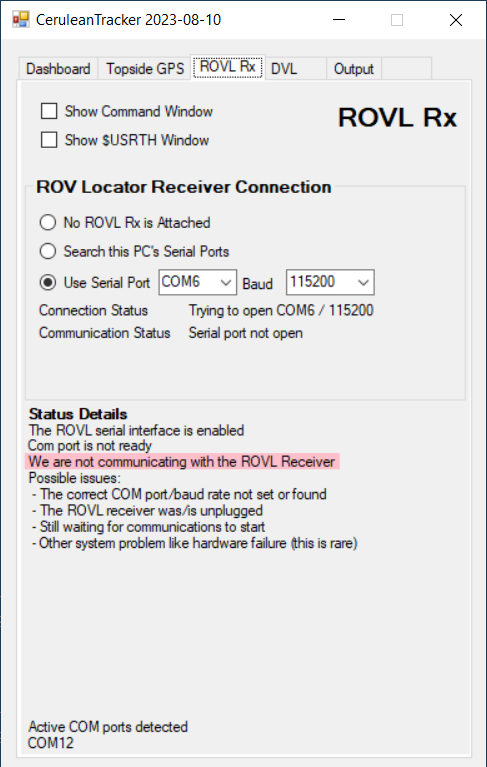
The most likely problem was the ROVL Rx was not plugged in. After plugging in the USB cable, the status changes to this:
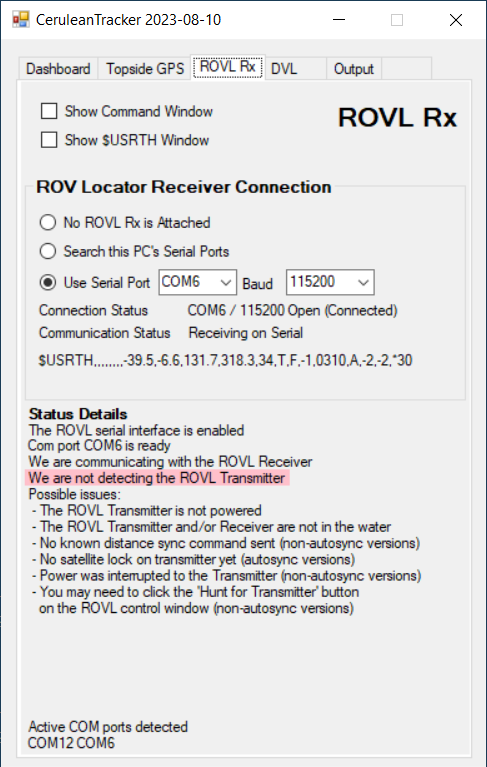
Now, CeruleanTracker has detected the ROVL Receiver on COM port 6 (the port number is assigned by Windows and may be a different number on your computer). Now we are talking to the receiver but it is not communicating with the transmitter/transponder. Some possible reasons are given in the status details area.
Note below the "Communication Status" label some text starting with "$USRTH,,,". CeruleanTracker shows the most recent message from the ROVL device in this location.
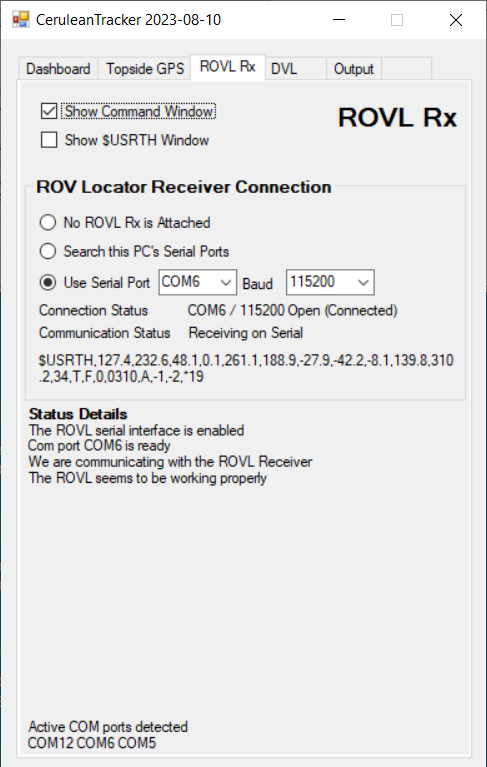
In this case, the problem was the transceiver and transponder (this is a Mk III system) were sitting on my desk as I typed this, and the transponder was not powered. After the transponder was powered and the two units were placed so they were touching, the status changes like this:
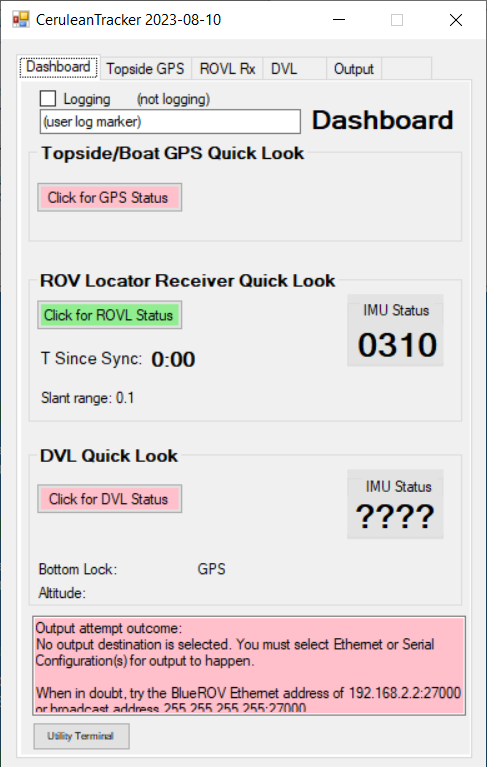
Looking back on the dashboard tab of the main window, we see the ROVL Locator Receiver status is nominally working: the status button is green, syncs are happening (in the Mk III the sync occurs each time a transponder response is detected, in the Mk II the sync occurs when the receiver gets GPS lock), the slant range is 0.1 meters (recall the units are on my desk touching), and the IMU is in need of calibration maneuvers.
More often, you will go through a structured troubleshooting guide like the one on the next tab.